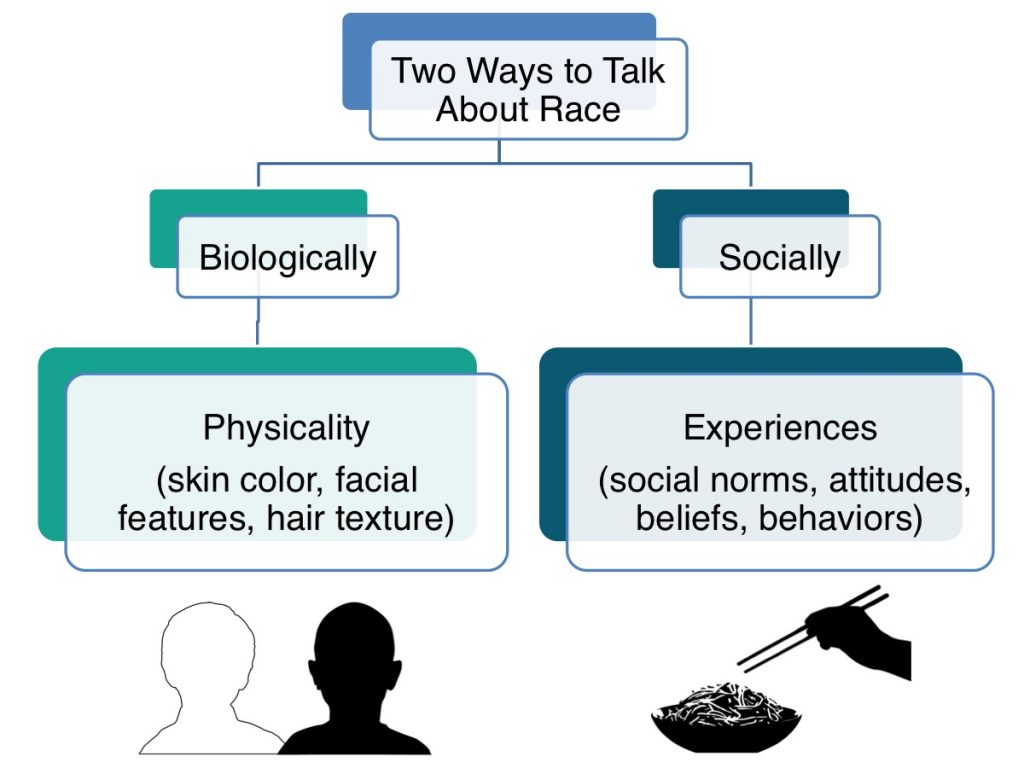
There are two common ways to talk about race: biologically and socially. Biological race refers to our physical features—our skin color, facial features, hair textures, and so on. Talking about race from a social viewpoint refers to how we experience race in terms of social norms, attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. In this Module, we are going to focus on the social impact of race on children. We will explore how race impacts the way children see the social world, how they understand who they are, and how they interact with others.
-
- Bias
- the belief that some people or ideas are better than others, usually resulting in unfair treatment
- Biological race
- physical racial features such as skin color, hair textures, and facial features
- Explicit racism/bias
- racism that is plainly expressed through words and or actions
- Implicit racism/bias
- racism that hides in our unconscious biases and gets expressed in our actions
- Racism
- the beliefs and practices that uphold and reinforce inequalities based on race
- Social identity
- a person’s sense of self that is based on group membership
- Social race
- The social norms, attitudes, beliefs and behaviors that accompany racial groups
- Systemic racism
- policies, practices, and laws that reinforce social inequalities by discriminating against groups of people, either directly or indirectly, and limiting their rights