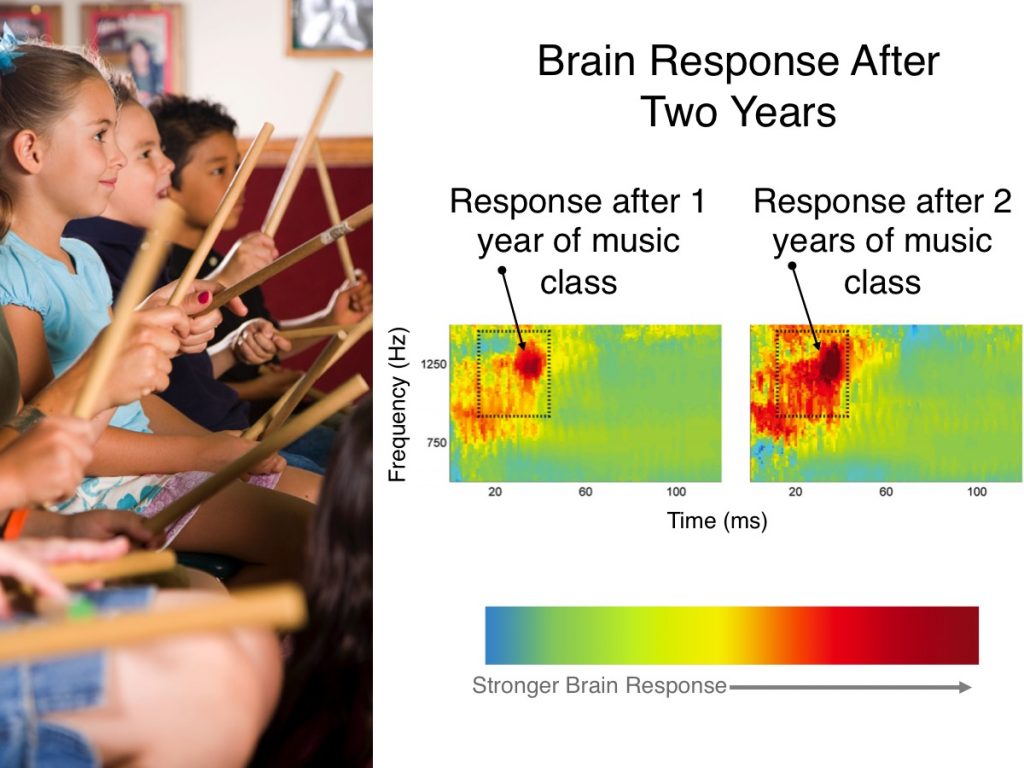
Researchers wondered whether early music training would influence language learning. Would musical training also give children a boost in their brain’s processing of speech sounds? They tested two groups of elementary aged children. Both groups participated in the same group music class curriculum. However, one group received two years of music class, while the other received only one year. In music class, children played instruments for an average of four hours a week.
At the end of each year, researchers measured the activity of the children’s brains. They wanted to know if there was a difference in how children’s brains processed consonant sounds. To do this, researchers used electroencephalography, or EEG. EEG is a technology that senses the weak electrical currents our brains produce when they are active.
At the end of the first year, there was no difference between the two groups. However, at the end of the second year, the group that had two years of music class showed significantly stronger brain responses to consonant sounds.
This study suggests that participating in group music classes can influence how children’s brains process speech sounds. It’s important to note that this didn’t happen overnight. Children participated in music classes for two years before there was a measurable effect.
On the next page, you will watch a video about a recent study on music learning in 9-month old infants.
-
- Beat
- the regular pulse of music
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- a non-invasive method used to measure electrical activity in the brain
- Executive function
- a set of mental abilities that help us focus attention, remember information, and switch between tasks
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- a non-invasive brain imaging technique used to determine which regions of the brain are active
- Meter
- a grouping of beats with specific patterns
- Neuroplasticity
- the ability to change how neurons in our brain are connected to each other
- Pitch
- the measure of how high or low we perceive sounds to be
- Pro-social behavior
- actions that are intended to help others
- Synchronized movement
- movements that occur in sync with musical beats and, or with other people
- Timbre
- the quality of a musical sound or voice that allows us to tell the differences between instruments or voices