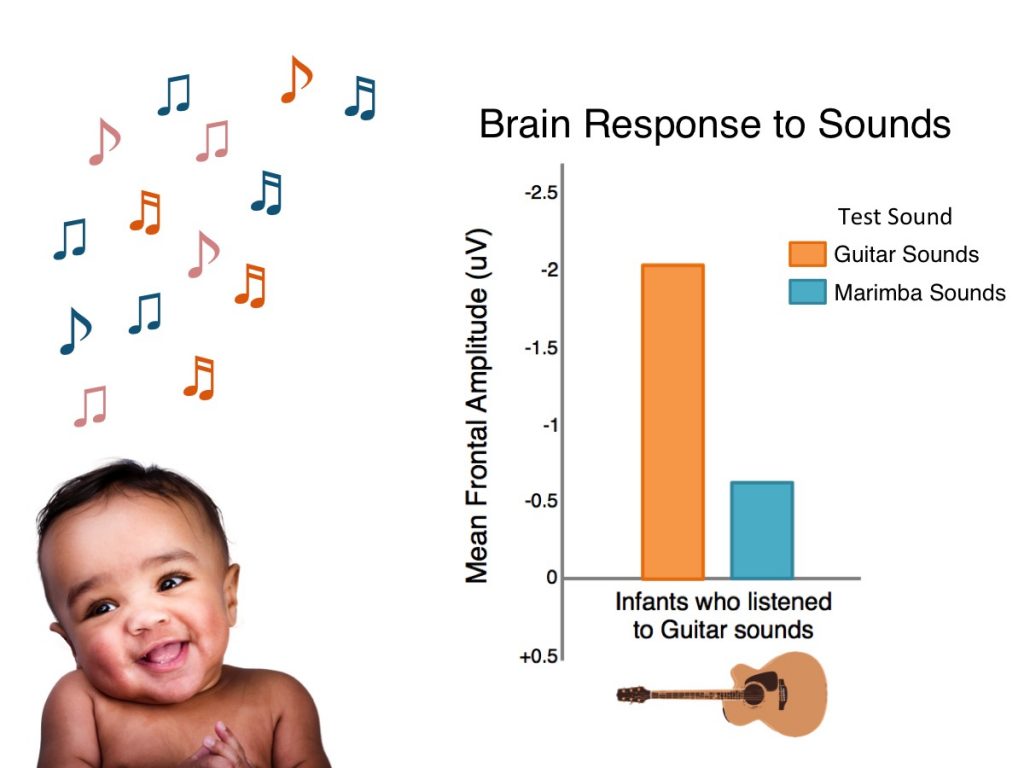
At an early age, children learn a lot about music in their culture. Even at four months of age, infants are learning complex information about the sounds in their environment. In one study, four-month-old infants heard 20 minutes of music everyday for one week. The music was either guitar music or marimba music.
As we just learned, guitar and marimba sound different; they each have a unique timbre. When the babies came into the lab, scientists measured their brain’s response to guitar and marimba sounds. To do this, the scientists used a non-invasive technique called electroencephalography or EEG. During EEG, babies are fitted with a snug cap, containing many sensors. The sensors detect the electrical signals the brain produces. Infants who listened to guitar music before their lab visit showed larger brain responses to guitar sounds. Alternatively, infants who listened to marimba music showed larger responses to marimba sounds.
This tells us that the brain is learning musical information very early in development. Infants learn just from listening to music in their environment and culture! What music do you like to play or sing along to? There is no evidence to support the idea that one type of music supports learning more than another.
Enjoying your favorite types of music with children is one of the best ways to introduce music into their lives.
-
- Beat
- the regular pulse of music
- Electroencephalography (EEG)
- a non-invasive method used to measure electrical activity in the brain
- Executive function
- a set of mental abilities that help us focus attention, remember information, and switch between tasks
- Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- a non-invasive brain imaging technique used to determine which regions of the brain are active
- Meter
- a grouping of beats with specific patterns
- Neuroplasticity
- the ability to change how neurons in our brain are connected to each other
- Pitch
- the measure of how high or low we perceive sounds to be
- Pro-social behavior
- actions that are intended to help others
- Synchronized movement
- movements that occur in sync with musical beats and, or with other people
- Timbre
- the quality of a musical sound or voice that allows us to tell the differences between instruments or voices