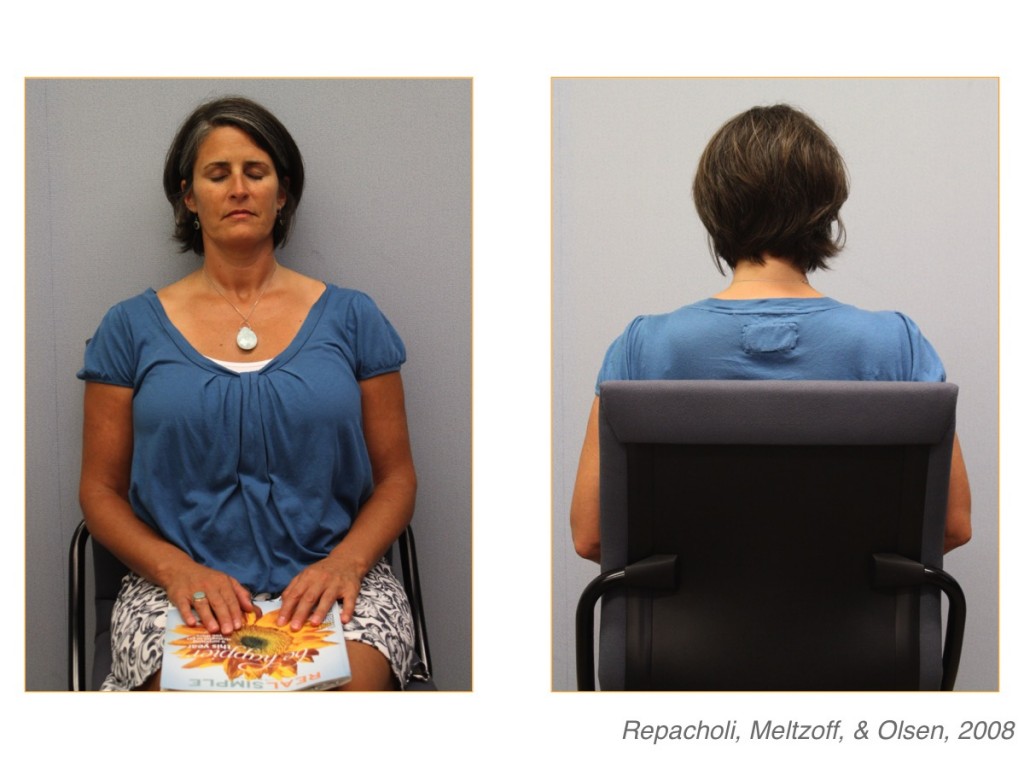
At this young age, children understood that they couldn’t make Nina angry if she wasn’t in the room to watch them push the button. Researchers wanted to investigate this further, so a new group of children watched the same emotional exchange you saw in the first video. Only this time, Nina stayed in the room and either closed her eyes or turned around in her chair before the child was given the toy. How do you think the child responded?
Surprisingly, children pushed the button on the toy even though Nina was still in the room. As adults, we understand that Nina would still be able to hear the buzzer on the toy and thus know we pushed the button, even if she wasn’t looking. However, these young children only pushed the button if they thought the adult (Nina) could not see them. At this age, eyes are an important part of infant communication. Young children were sensitive to whether the angry adult was watching their actions. It is only as children grow up that they learn that other people can still hear us even if they aren’t looking at us.
In these scenarios, you may have noticed that Nina was using big words (such as “that’s aggravating”) that a young child wouldn’t understand. But the children listened to Nina’s tone of voice and watched her eye gaze and facial expressions to understand that Nina did not like the buzzer noise on the toy. The children then used this information in combination with Nina’s availability in the room to decide whether or not to push the button.
During their second year of life, children can use emotions that are not directly communicated to them to learn about rules in their family, society and culture. Children are learning all the time simply by observing and listening to the people around them.
-
- Dyadic interaction
- a back-and-forth exchange between caregiver and child
- Self-regulation
- the ability to control our behaviors, emotions, and impulses
- Social emotional development
- learning to express and manage emotions and form positive relationships
- Social referencing
- looking to an adult for emotional information in an uncertain situation
- Triadic interaction
- a back-and-forth exchange between caregiver, child, and object